Regenerative agriculture or regenerative farming is a model of crop or livestock production that uses a variety of practices to restore and conserve ecosystems connected to the land. While at the same time seeks to increase productivity and mitigate environmental impacts like climate change and biodiversity loss.
Regenerative agriculture both encompasses traditional, proven practices as well as innovation in management, measurement and practice. It is an alternative way of raising crops and animals that, by working with natural systems, ensures the long-term viability and resistence of the land to continue to provide for generations to come. The focus on restoration and regeneration of nature is about ‘doing more good’ through agriculture, rather than just ‘less bad’.
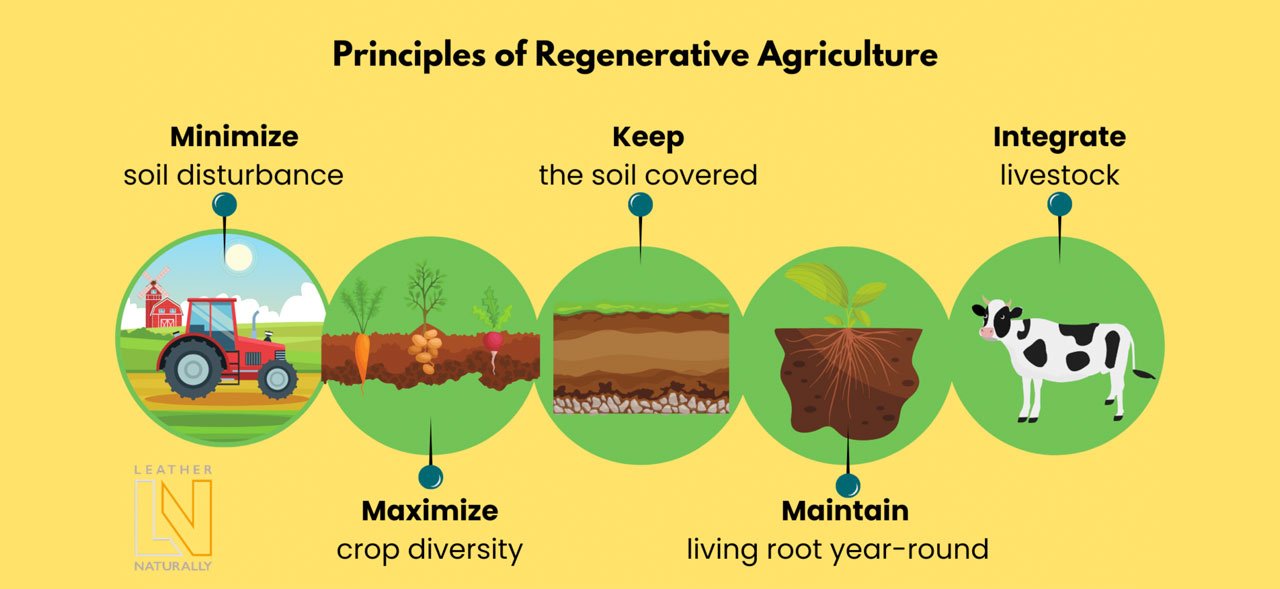
Regenerative agriculture distinguishes a kind of farming that goes beyond simply sustainable as it seeks to improve ecosystem services within farming systems. Rather than a set method or simply sustainable farming, regenerative agriculture consists of a multitude of (holistic) farming practices to improve soil health and reverse climate change by expanding biodiversity, improving the water cycle, increasing organic matter in soil structure and transferring carbon from the atmosphere to the soil. For example, it can also include grazing practices that, among others, reverse climate change by rebuilding soil organic matter and restoring degraded soil biodiversity. Doing so, regenerative agriculture acknowledges the role that livestock plays in sequestering carbon in the soil and the relationship of this to soil health.
Check out the full article at www.leathernaturally.org